Embarking on a journey into the world of forex trading can be both exciting and daunting, especially when faced with a myriad of terms that may seem like a complex puzzle. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify essential forex terms, providing a solid foundation for traders to navigate the dynamic landscape with confidence.
Pips (Percentage in Point):
- Definition: Pips represent the smallest price movement in the forex market. It is typically expressed as a four-decimal-point value. It is a crucial concept for measuring price changes, allowing traders to track and analyze market fluctuations. For most currency pairs, a one-pip movement occurs in the fourth decimal place, except for currency pairs involving the Japanese Yen, which is the second decimal place. Understanding pips is essential for evaluating price movements, setting stop-loss and take-profit levels, and calculating potential profits or losses in forex trading.
- Example: If the USD/JPY moves from 110.50 to 110.51, it has experienced a one-pip movement.
Leverage:
- Definition: Leverage allows traders to control a larger position size with a smaller amount of capital. It magnifies both potential gains and losses. Leverage in forex trading is a financial tool that enables traders to control a larger position size with a relatively smaller amount of capital. Expressed as a ratio (e.g., 50:1), it signifies the relationship between the trader’s borrowed funds and their capital. While leverage can magnify potential profits, it also amplifies the risk of losses, making risk management crucial. Traders should use leverage judiciously, understanding its impact on positions and the importance of maintaining adequate margins to avoid margin calls. Successful navigation of leverage requires a delicate balance between maximizing trading potential and protecting one’s capital.
- Example: With leverage of 50:1, a trader can control a position worth $50,000 with only $1,000 of their own capital.
Liquidity
- Definition: Liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset, such as a currency pair, can be bought or sold without causing a significant price change. Liquidity in the context of forex trading refers to the ease with which a currency pair can be bought or sold in the market without causing a significant impact on its price. High liquidity is desirable because it typically results in narrower bid-ask spreads, reduced slippage, and smoother execution of trades. Major currency pairs and those involving strong economies often exhibit high liquidity. Traders benefit from liquid markets as they provide more opportunities to enter or exit positions at desired prices, enhancing overall efficiency and flexibility in trading strategies. Monitoring liquidity levels is essential for making informed trading decisions and managing risk effectively in the dynamic forex market.
- Importance: High liquidity is desirable as it often leads to tighter spreads, reduced slippage, and smoother trade execution.
Spread
- Definition: The spread is the difference between the bid (sell) and ask (buy) prices of a currency pair. It represents the broker’s fee for facilitating the trade. It represents the cost incurred by traders for executing a trade and serves as compensation for the broker facilitating the transaction. A lower spread is generally favorable for traders as it reduces the overall cost of entering and exiting positions. Tighter spreads are often associated with higher liquidity and a more efficient market. Traders should consider spreads when evaluating the cost-effectiveness of their trades and choose brokers that offer competitive and transparent pricing. Efficient management of spreads is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and maximizing potential profits.
- Impact: Lower spreads are favorable for traders as they reduce the cost of entering and exiting positions.
Margin
- Definition: Margin is the amount of money required to open and maintain a leveraged position. It is expressed as a percentage of the total trade size. Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital. While margin amplifies potential profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses. Maintaining a sufficient margin level is crucial to avoid margin calls, which occur when the account balance falls below the required minimum. Traders should use margins carefully, considering risk management strategies to protect their capital and ensure responsible trading practices. Understanding and managing margins is essential for navigating the complexities of leveraged trading in the forex market.
- Caution: While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of substantial losses, emphasizing the importance of prudent margin management.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit:
- Definition: Stop-loss is an order placed to limit potential losses, while take-profit is an order to secure a specified profit level.
- Strategy: Setting these orders is crucial for risk management and disciplined trading, helping traders protect capital and lock in gains.
Currency Pair:
- Definition: A currency pair consists of two currencies, where one is quoted against the other. The first currency is the base, and the second is the quote or counter currency.
- Example: In the GBP/USD pair, GBP is the base currency, and USD is the quote currency.
Risk-Reward Ratio:
- Definition: The risk-reward ratio is the relationship between the potential profit and potential loss of a trade. It is a key metric for assessing the viability of a trading strategy. The Risk-Reward Ratio is a fundamental concept in trading that quantifies the potential profit against the potential loss in a trade. It is expressed as a ratio, typically denoted as 1:2, 1:3, etc., where the first number represents the potential reward, and the second number represents the potential risk. For example, a 1:2 risk-reward ratio means that for every unit of risk undertaken, the trader aims for a reward that is two times that amount. A favorable risk-reward ratio is a critical component of a sound trading strategy, as it helps traders assess the viability of a trade and ensures that potential profits outweigh potential losses. Successful traders often strive for risk-reward ratios that align with their overall trading objectives and risk tolerance.
- Importance: A favorable risk-reward ratio helps traders ensure that potential profits outweigh potential losses, contributing to a robust trading approach. PreferForex provided signals that are always a minimum of 2:1 to 8:1 that secure trading accounts, and earn decent profit.
Below you can understand clearly the risk-reward in the MT4 terminal – It is one of our signals execution for premium members-
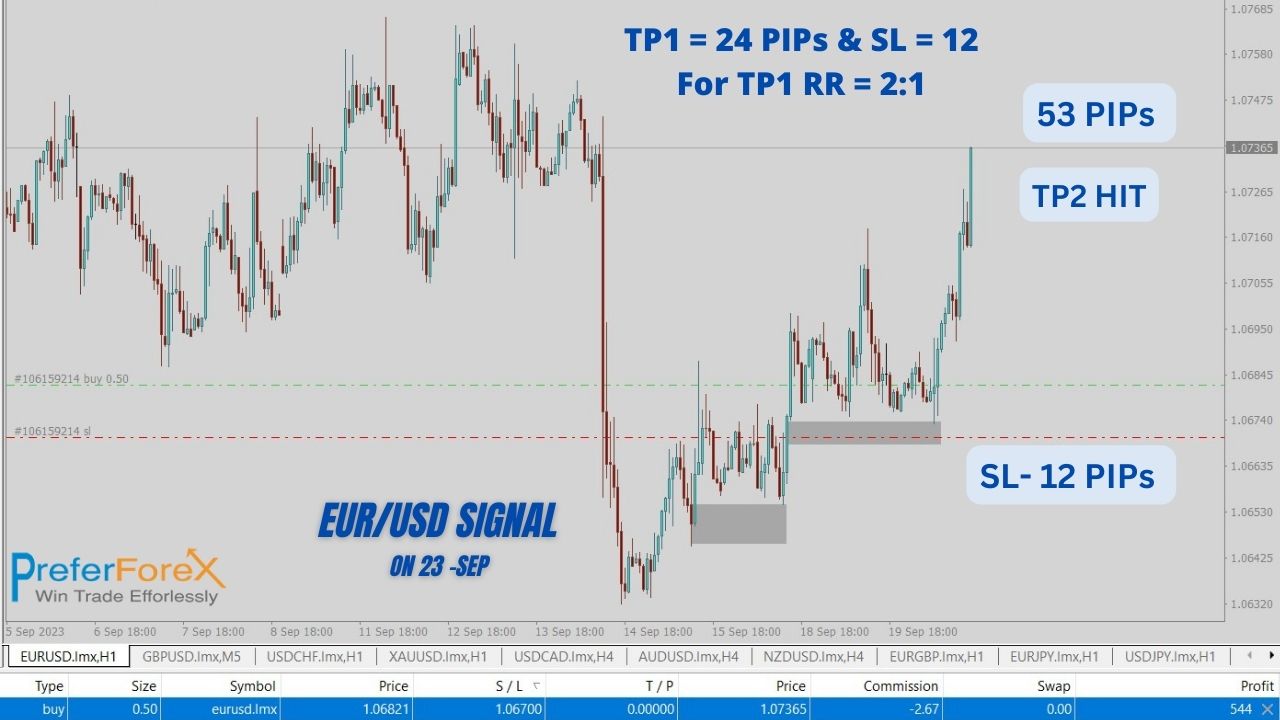
Market Order:
- Definition: A market order is an instruction to buy or sell a financial instrument immediately at the current market price.
- Execution: Market orders are executed at the best available price in the market, providing speed but not price certainty.
Candlestick Chart
- Definition: A candlestick chart is a type of financial chart used to represent price movements in the forex market. It consists of individual “candles” that provide information about the open, high, low, and close prices for a specific period. A Candlestick Chart is a type of financial chart used in trading to represent the price movements of a financial instrument, such as a currency pair in forex. Each “candlestick” on the chart provides information about the opening, closing, high, and low prices for a specific time period. The body of the candlestick is typically filled or hollow, representing the price range between the opening and closing prices. Candlestick charts are widely used for technical analysis in financial markets as they visually convey market sentiment and help traders identify patterns and trends. Various candlestick patterns are recognized and interpreted to make informed decisions about potential market entry and exit points, contributing to the development of effective trading strategies.
- Analysis: Traders often use candlestick patterns to analyze price trends and make informed decisions about market entry and exit points.
Conclusion: Equipped with a solid understanding of these key forex terms, traders can navigate the complexities of the foreign exchange market more confidently. Continuous learning, coupled with practical experience, is essential for those seeking success in the ever-evolving world of forex trading. To start trading you can get our expert hand it is completely free try professional forex signals for 15 days! Happy trading

